- SOLUTIONS
- PRODUCTS
- SERVICES
- PARTNERS
- RESOURCES
Choosing Between 40G QSFP SR4 and BiDi: Your Comprehensive Guide

Discover the 40G QSFP+ BiDi Module

Unlocking Seamless Connectivity: Starlink and Peplink Partnership Takes the Lead
Comprehensive Guide - Choosing 40G QSFP SR4 and 40G QSFP BiDi
In the ever-evolving landscape of high-speed data transmission, the selection of the right transceiver module plays a pivotal role in achieving a seamless network deployment. Among the myriad options available, two commonly employed modules for short-distance transmission (<1km) are the 40GBASE-SR4 and 40GBASE-BiDi. This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the mysteries surrounding these modules, exploring their characteristics, differences, and providing insights to help you make informed decisions for your 40G network deployment.
40G QSFP BIDI SR Optical Transceiver Module
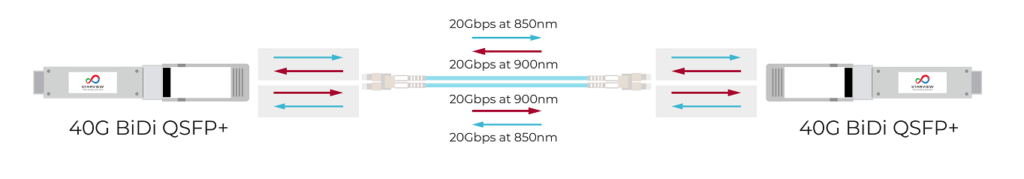
Let’s commence with the 40G QSFP BIDI SR optical module, a solution leveraging two 20G channels for efficient 40G transmission. This module employs Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology, enabling the simultaneous transmission and reception of optical signals on a multi-mode fiber at distinct wavelengths, typically 850nm and 900nm. Notably, the SV-QSFP-40G-SR2 can cover up to 100m with an OM3 fiber jumper and extend to 150m when paired with an OM4 fiber jumper. This flexibility facilitates the rapid establishment of a 40G network, proving particularly advantageous during upgrades from a 10G setup. It’s crucial to note that the 40G QSFP BIDI SR requires deployment in pairs for optimal performance.
40G QSFP SR4 Optical Transceiver Module: Four Channels of 10 Gbps Parallel Transmission
The 40GBASE-SR4 optical module (SV-QSFP-40G-PSR4 optical module) adheres to the IEEE 802.3BA 40GBASE-SR4 standard and adopts the MPO/MTP interface. When used with OM3 optical fibers, it achieves a maximum transmission distance of 100m, extending to an impressive 150m with OM4 optical fibers.

The 40G QSFP SR4 optical module features four independent optical signal transmitting and receiving channels, each supporting a rapid 10 Gbps data transmission rate. Typically used with a 12-core MTP/MPO fiber jumper, this module allocates four cores for transmitting, four for receiving, with the middle four cores remaining idle. Additionally, achieving 4x10G transmission is possible by connecting an 8-core MTP-LC branch cable.
Differences Between 40G SR4 and BIDI:
To make an informed decision, let’s compare the 40G SR4 and BIDI modules:
Transceiver Module | 40G SR4 | 40G BIDI |
Connector | MTP/MPO | Duplex LC |
Cable Type | MMF | MMF |
Wavelength | 850nm | 832nm-918nm |
Transmission Distance | 150m@OM4 100m@OM3 | 150m@OM4 100m@OM3 |
Whether 4 x 10 G links are supported | Yes | No |
10G Upgrade to 40G: How to Choose:
When contemplating an upgrade from 10G to 40G, the choice between 40G SR4 and BIDI depends on the network structure:
Unstructured Cabling Systems:
- In setups where fiber jumpers directly connect devices, the 40G QSFP BIDI SR seamlessly integrates into existing 10G cabling systems. By reusing LC multi-mode fiber jumpers, this module provides a cost-effective upgrade to 40G, minimizing cabling costs.
Structured Cabling Systems:
- For more flexible data center layouts using structured cabling, the 40G QSFP SR4 may be preferred. While requiring some changes, such as replacing LC fiber jumpers with MTP jumpers, it offers a broader range and adaptability within the structured cabling framework.
Summary:
In summary, the 40G QSFP BIDI SR excels in upgrading from 10G to 40G without necessitating an overhaul of existing cabling infrastructure, offering high flexibility and simplicity. On the other hand, the 40G QSFP SR4 finds its niche in 40G to 10G network transmissions, utilizing an 8-core MTP-LC fiber jumper.
Conclusion:
Choosing between the 40G QSFP SR4 and BIDI involves weighing factors such as existing infrastructure, deployment scenarios, and future scalability. By understanding the nuances of each module, you can make informed decisions that align with your network requirements, ensuring a smooth and efficient 40G deployment.
Stay Informed with Our Newsletters
If you missed our previous newsletters focusing on our optical modules, you can catch up by visiting these links: