- SOLUTIONS
- PRODUCTS
- SERVICES
- PARTNERS
- RESOURCES
Is RAID Dead?- Part 1

The Future of Software Defined Storage is Now

Is RAID Dead?- Part 2
Is RAID Dead?- Part 1

30+ years of deployment and evolution
Primer on RAID
RAID is a storage system, made up of many independent HDDs, forming a large logical storage pool. There are a few RAID methods in use today, with each one providing different capacities and failure options. We will explain how the different RAID methods work, and how they handle drive failures.
RAID 0
RAID 0 combines 2 similar capacity drives to form a single logical drive, with the total capacity of 2 drives combined. The diagram below illustrates RAID 0:
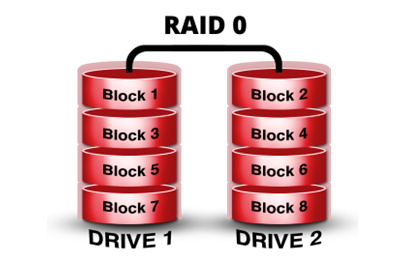
- Data is written across the 2 drives.
- The 2 drives are combined to form 1 logical drive with twice the capacity of 1 drive.
- There is no failure option.
- A drive failure is catastrophic and will mean data loss.
RAID 1
RAID 1 combines 2 similar capacity drives to form a single drive, with the total capacity of 1 drive. The diagram below illustrates RAID 1 :
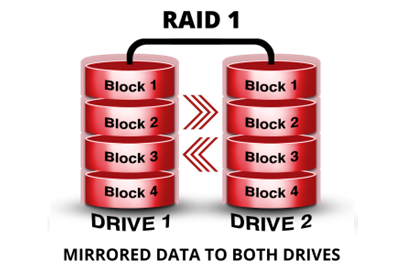
- Data is written to 1 drive and mirrored to the other drive. The 2 drives are combined to form 1, logical drive, but with the capacity of only 1 drive.
- 1 drive can fail, and operations can continue uninterrupted.
- The failed drive can be replaced with a new one while the system is running.
- Once replaced, the data will be copied to the new drive.
RAID 5
RAID 5 combines 3 or more similar capacity drives to form a single logical drive. It can tolerate any 1 drive failure within the RAID set, without interruptions or data loss. The diagram below illustrates RAID 5.
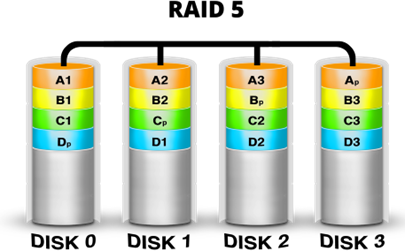
In this example, there is a total of 4 drives in a RAID 5 set. A chunk of data is broken up into 4 smaller shards, eg A is broken up into A1, A2, A3, Ap, and written across the drives. A can be read back, as long as any 3 of the 4 shards are available, therefore RAID 5 can suffer any 1 drive failure without interruption or data loss.
The total usable capacity is (N -1) x C, where N is the number of drive, and C is the capacity of each drive. The failed drive can be replaced with a new one while the system is running. Once replaced, the data will commence rebuilding.
RAID 6
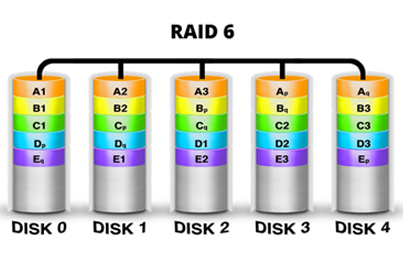
RAID 6 combines 4 or more similar capacity drives to form a single logical drive. It is similar to RAID 5, but it can withstand 2 drive failures. The diagram below illustrates RAID 6.
RAID 10, 50, 60
RAID 10, 50 and 60 is a hybrid between RAID 1/5/6 with RAID 0. It offers higher reliability and faster rebuilding times during drive failures, but with a higher overhead of unusable space. If you are interested to know more about these advance RAID, let us know, and we will be happy to write another Insight article about it.
Replica and Erasure Coding
In modern SDS, RAID is no longer used, instead alterative technologies such as Replica or Erasure Coding is used. This is discussed in part 2 of this series of Insight, so make sure you follow our Facebook or LinkedIn.
RELATED ARTICLES
Is RAID Dead? Part 1
Is RAID Dead? Part 2
Is RAID Dead? Part 3
